Class 5 Call Manager (C5CM)
The Clarent® Class 5 Call Manager (C5CM) is part of the IPVision architecture that supports Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP) transmission in a Class 5-style deployment. C5CM is commonly used on VoBB applications, as well as wholesale (traffic termination) , and it can also work with Border Agent to perform Nat transversal and topology hiding. It’s IVR functionality is greatly used for prepaid applications, including VoBB prepaid customers.
Providing call control and supplementary service execution to distributed or centralized media gateways, the Clarent® Class 5 Call Manager is a highly functional, standards-based Media Gateway Controller for use in consumer, enterprise, and tandem switching applications. Based on the MGCP H.323 and SIP protocols, the Clarent® Class 5 Call Manager provides call control functionality to MGCP-based edge devices, H.323 LRQ interconnection to other Gatekeepers, SIP proxy, and GK to control H.323 Gateways.
⁃ MGCP-Media Gateway Control Protocol controls CPE gateways (FXS). MGCP specifies standards-based protocols to manage MGCP endpoints and establish connections
⁃ SIP-Session Initiation Protocol controls the Clarent NetPerformer (FXO, FXS, E1, T1) and SIP user agents
⁃ H.323-H.323 protocol that the C5CM uses to interoperate with H.323 access gateways (FXS, FXO, E1 and T1)
⁃ RTP-Real-time Transport Protocol streams media between Clarent Announcement Servers and CPE gateways, and CPE gateways and other Clarent products, such as the Class 4 Call Manager (C4CM)
⁃ SNMP-Simple Network Management Protocol monitors and configures the C5CM via a network Management system
⁃ NCS-Network-based Call Signaling protocol is similar to MGCP 1.0 and is specified by the PacketCable consortium
⁃ XML-Extensible Markup Language, a standards-based protocol that delivers information to disparate systems as a common data format
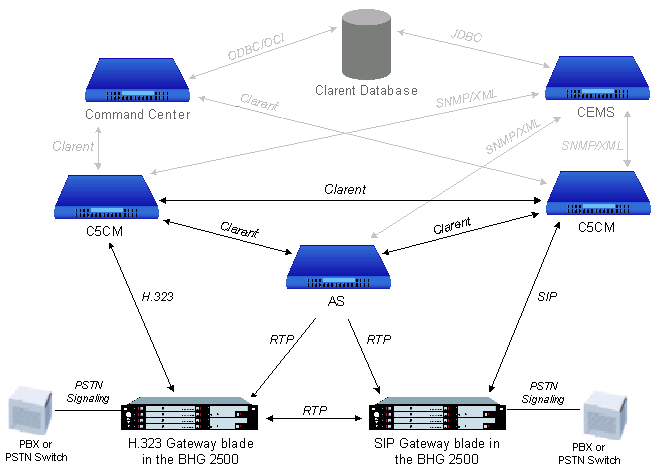
The Clarent® Class 5 Call Manager can also interface to SS7 networks (through the Clarent® Class 4 Call Manager and Clarent SS7 Gateway), H.323 Gateways, SIP-enabled gateways and appliances and other standards-based applications.
The Clarent® Class 5 Call Manager starts with the Service Editor employed in today’s Clarent Carrier Gateway and adds basic call control features that enable edge devices to appear as “ports” in a Viasat’s network. These ports acquire all of the advanced features available in today’s Viasat networks, such as subscriber domains, service classes, dynamic routing, customized rating plans and billing data collection.
Basic CLASS features are available now allowing the Class-5 Call Manager to support local services for both business and residential subscribers. The C5CM is also responsible for codec selection, which can be determined based on several criteria-such as on a per-subscriber or per-network basis.
The C5CM is available on UNIX platforms, on Sun Solaris 2.8 for network-based deployments, allowing N+1 redundant configuration.
The C5CM controls access to the Viasat network and handles signaling for Customer Premises Equipment (CPE) gateways supporting FXS, FXO and digital telephony connections. C5CM 3.0 offers call management for MGCP, H.323 and SIP access gateways. This capability, along with C5CM’s support of MGCP and SIP gateways, establishes the C5CM as a foundation to support enterprise voice/fax/data services.
C5CM Multiple Applications Scenarios
C5CM acts as a call agent for third-party residential and enterprise gateways, and SIP user agents. The C5CM can also facilitate interoperation of CPE gateways and enterprise access gateways with Clarent C4CM installations to connect to traditional circuit-switched networks.
Residential CPE Gateways
The C5CM uses SIP and MGCP protocols to control CPEs connected directly to endpoint devices such as telephones, fax machines (FXS) and modems. The different kinds of CPGs are:
- Ethernet CPEs: Ethernet CPEs are a kind of stand-alone customer premise devices that provides VoIP capabilities for any access technology. Deployed with an access-specific broadband device, the Ethernet CPEs offers an instant solution for any variation of technologies.
- Cable CPEs: Clarent has taken its commitment to standards-based development into the emerging market of voice-over-cable. PacketCable standards drive the development of integrated VoIP and Cable modems at Clarent. This devices are mainly cable modems with analog interfaces to connect to normal telephone lines to provide VoIP services to SOHOs or residential.
- DSL CPE: DSL CPE devices support basic implementations as well as additional features such as routing capabilities for small business implementations.
- IP Phones: Clarent has developed and ensured the interoperability of several IP Phones. These phones match the broad range of capabilities of high-end PSTN phones, such as speakerphone, speed dialing, and caller name display.
Basic Subscriber Services
- Call Forward All: automatically forwards all calls to another telephone number.
- Call Forward Busy: when the dialed number is busy, automatically forwards the call.
- Call Forward No Answer: when the call is unanswered after a specified number of rings automatically forwards a call.
- Caller ID: on a telephone with display capabilities, displays the name and phone number of the incoming call.
- Caller ID Blocking: automatically prevents the subscriber’s telephone number (ANI) and name from being transmitted to a Caller ID device. This feature can be disabled on a per-call basis.
- Call Return: allows a subscriber to dial and call the telephone number of the last caller.
- Speed Dial: Enables a subscriber to program shortcut dialing sequences to dial specified numbers.
- Call Waiting: allows a subscriber to place the current call on hold and answer an incoming call.
- Selective Caller ID Blocking: enables a subscriber to block Caller ID information from being transmitted to the called number. This feature can be enabled on a per-call basis.
- Caller ID on Call Waiting: on a telephone with display capabilities, displays the name and telephone number of an incoming call while another call is in progress.
- Customer Originated Trace: allows the subscriber to flag the last call received, for documentation of harassment or other action by authorities or network administration personnel.
